What Is the Best Communications Solution for My Business?

Sandra Palumbo, research fellow, reports into Yankee Group’s Research Council. Her research focuses on cloud computing, enterprise mobility and service provider strategies, with particular emphasis on software as a service (SaaS), mobile applications, Web portals, managed services, professional services and wholesale.
Picking the Right Communications Solution for Your Business Is Critical in This Fast-Paced World
Businesses large and small continue to evolve their communications infrastructure in an attempt to garner the greatest benefits from the latest technologies. Today, the technology options available to businesses of all sizes are greater than ever before. Instead of just choosing between a managed service and a traditional on-premises deployment of a communications solution, we now have cloud delivery as an option. The move to communications and collaboration applications is not just thought of in terms of office worker use, but mobile worker use as well. Security, reliability, performance and flexibility are solution criteria that are now more important than ever before in a highly competitive, rapidly evolving world.
History shows that while many companies struggle with choosing the best communications solution for their business, other companies enamored with the promise of the latest technologies move quickly to adopt them without considering how those new solutions fit into their existing infrastructure and if they will truly benefit the business and its employees.
Enterprises are rapidly extending beyond their physical borders and to be successful, businesses must be able to communicate and collaborate with their employees, partners and customers, no matter where they are located. Implementing technology solutions that are easy to adopt and can scale to meet the needs of the business today and tomorrow is a real challenge for any IT department looking to stay competitive in today’s marketplace (see image 1).
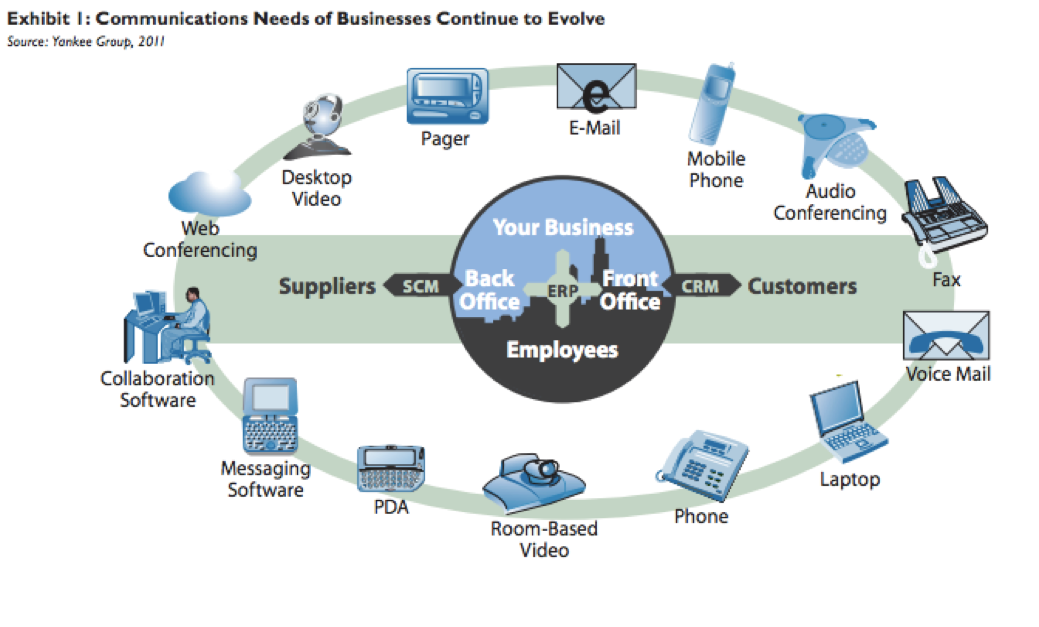
This report examines the evolution of communications services and their associated underlying technologies. Specifically, we analyze the architectural and feature evolution of managed/hosted telephony, VoIP, IP trunking and unified communications (UC). Additionally, we present key decision criteria for selecting the right IP telephony solution for a particular business.
The Evolution of Managed and Hosted Telephony
In today’s complicated technology world, the terms “managed telephony” or “hosted telephony” can often refer to a variety of solutions. Yankee Group defines VoIP/IP telephony as the use of business-class voice and multimedia applications provided through IP telephony systems, handsets and software. When the terms “managed” or “hosted” are added to “VoIP,” “telephony” or “IP PBX,” we are referring to businesses using a third-party service provider to manage and maintain at least some aspect of the voice service. Typically, this includes the monitoring and management of any hardware and software required to make the voice solution work. Managed solutions typically involve some on-premises equipment and hence remote management and monitoring, while hosted services are typically more cloud-based or hosted at the service provider’s location.
As enterprises come to terms with the business challenges that prevent them from reaping the benefits of IP telephony and UC solutions, it becomes time for these businesses to understand what solutions exist for overcoming these challenges and leveraging today’s IP networks. Because the underlying network is based on IP, IP telephony solutions can be located anywhere within the network reach, including the telecommunications provider’s cloud or hosting/data center. This allows for the possibility of a business offloading some of the day-to-day management and maintenance work to a service provider. A managed or hosted model is typically a most intriguing option for small and midsize enterprises because they don’t have the same staff expertise or balance sheet flexibility as larger enterprises.
From an economic or cost standpoint, a managed/hosted service is typically less front-end loaded with capital expenditures for equipment. Instead, a monthly service fee is billed over the typical three-year course of a contract. A managed/hosted service also offers savings in terms of time and productivity for IT staff, since most of the day-to-day management and maintenance work is handled by the service provider, meaning internal IT staff can focus on more strategic IT priorities and projects. This lets businesses with small in-house IT staffs do much more with the resources they have.
Many businesses that turn to managed/hosted IP telephony services already have some history with outsourcing and view it as a strategic business priority. With the emergence and adoption of cloud-based services, companies that are newer to outsourced services may find this the perfect time to consider a managed or hosted solution. As more applications are pushed to the cloud, a managed service can be a great first step and foundation for future communications and collaboration application adoption that doesn’t require a lot of heavy lifting from the internal IT staff every time something new is deployed.
Yankee Group’s Anywhere Enterprise: 2010 US Unified Communications (UC) FastView Survey proves that for enterprises, speed and savings are the primary drivers for the move to managed and hosted IP telephony and UC solutions (see Exhibit 2). Enterprises are looking to save on IT maintenance, integration between multiple providers and infrastructure costs. These drivers tie nicely into the value proposition behind all managed and cloud-based or hosted services. Businesses also can benefit from the hosting/managed service provider’s road map for the evolution of available services and applications. It often is easier to undertake technology improvements and refreshes when using a managed service because those arrangements can be worked into the agreement upfront, without having to renegotiate or wait for a contract period to end.
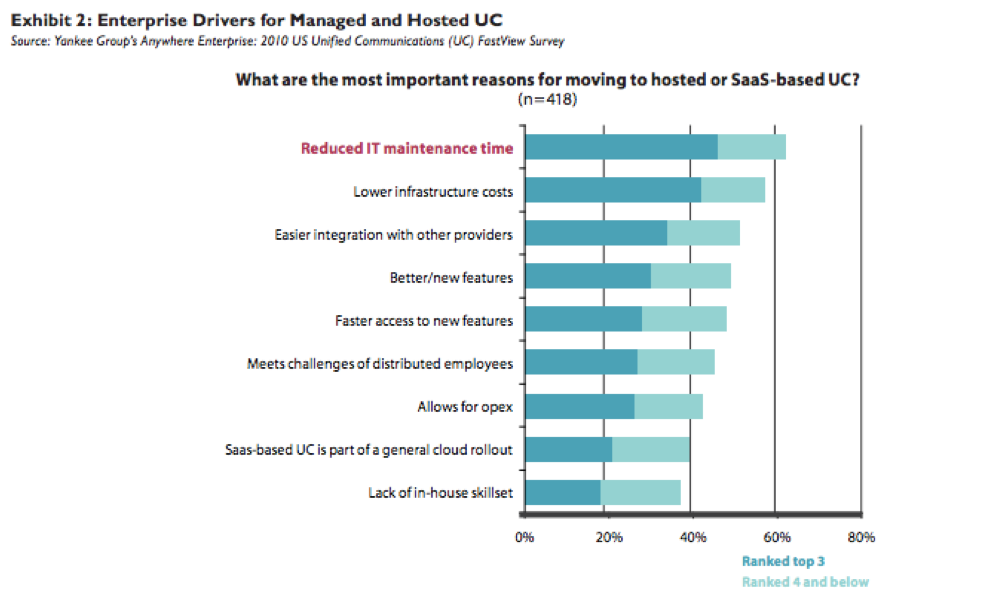
Concerns around a perceived lack of cost savings require some upfront conversations between businesses and their potential providers. Providers and businesses need to work together to identify the best IP telephony solution for a given business, whether it’s fully managed, a cloud-based hosted solution, a more traditional on-premises deployment or a hybrid. Every business will have different needs and goals, and service providers need to partner with businesses in putting together the right solution. Even when cost isn’t the concern but something such as reliability or performance is, VoIP’s benefits are no different in a managed arrangement as in a traditional one and need to be addressed as part of the initial solution plan and architecture.
If cost savings are an overall driver, the business must work with its provider to build a detailed cost assessment of VoIP and UC solutions, bearing in mind the business’ current and future communications environment. This ensures there will be no surprises when the bill arrives each month. Managed/hosted solutions can provide some savings over traditional deployments, but savings aren’t guaranteed until the enterprise architecture is really analyzed and evaluated. In a later section of this report we provide some detailed guidance for areas of consideration in selecting your service provider and solution.
The Benefits of Consolidated Trunking
Despite its benefits, managed and hosted telephony solutions may not be the answer for every business. For companies that choose to keep the IP PBX on their own premises, an architectural change that can have immediate cost savings is to move to consolidated IP trunks. Typically, VoIP is deployed on a node-by-node basis, with each location having its own call control and voice infrastructure. This means each location has its own trunks for calls out to the PSTN. In some cases, multiple trunks may be required for redundancy purposes. This architecture can result in a very high cost together with very low trunk utilization.
An alternative architecture choice is to centralize call control either in a central data center or corporate headquarters and then leverage the corporate WAN to distribute call control. This provides companies with the ability to consolidate trunking services to fewer locations. It also gives organizations the option of using higher bandwidth trunks that can carry more calls, which translates to fewer lines to terminate.
By adopting an IP trunking architecture, businesses can capitalize on the many core strengths of IP solutions, particularly when compared to traditional PSTN voice solutions. In addition to consolidation, these improvements and benefits include:
- Better network reliability than traditional PSTN solutions. The idea that VoIP is any less reliable than traditional voice is one of the biggest myths holding back greater adoption. IP is a resilient protocol and reliability can be built into the design. For example, instead of having separate voice and data networks, a company could choose to deploy two data networks that act as a backup for one another. This would cost no more than the traditional model but could protect against any network outage. It would also provide better disaster recovery capabilities than running separate networks.
- Lower intra-enterprise calling costs. All on-net calls (that is, calls within a corporation) are kept on the corporate data network, meaning the cost of these calls can be eliminated altogether or at least greatly reduced, depending on architecture. Cost savings will vary by organization type. A large, distributed multinational company will save orders of magnitude more than a large company located in a single building.
- Faster deployment of UC applications. Particularly when a centralized architecture is adopted, new UC applications can be deployed in the central location and then distributed to all users over the company network. This can improve the time to market of new applications by orders of magnitude compared with the node-by-node deployment of traditional communications applications.
In these tough economic times, businesses are trying to improve profitability and reduce costs, and they are forced to look for ways to save when it comes to their communications expenses. Additionally, companies with smaller IT organizations must look for new, less staff-intensive ways of solving problems. The right IP telephony solution helps companies achieve the following benefits:
- Reduced overall communications costs
- More efficient use of network assets
- Optimized trunking to match a company’s calling patterns
- Accelerated deployment of current and future UC applications through the simplification of network design
- Higher reliability and better disaster recovery capabilities than traditional TDM-based systems
VoIP is the direction every business is moving in and will eventually adopt. The key for businesses today is to find the right solution and the right service provider partner to deliver that solution to their business. And while the decision to move to VoIP may be an easy and straightforward one, choosing the best solution and solution provider can be a bit more complicated.
Finding the Right VoIP Solution
Businesses that do their homework in preparation for the adoption of a VoIP solution will find the decision an easy one. These businesses will also discover that VoIP and UC will benefit their business in many more ways than just cost savings. They bring tremendous productivity and collaboration improvements as well. IP trunking is the most cost-effective method of creating a scalable IP telephony and ultimately UC deployment, and it has benefits beyond those of PSTN trunking. The key to true success, however, is finding the best service provider for your company. What are the key considerations when making the decision?
For every business and situation, the answer varies, but Exhibit 3 offers a guide to better understand the areas for consideration and evaluation in selecting the right solution. We break the table up into two key components—voice and data—because a VoIP solution requires that companies not only have a handle on their voice costs but also their data costs, since the move to VoIP is a move toward convergence. When evaluating new solutions, companies must also understand their current costs (recurring, capital and operating) and be able to compare that to the expected new costs of the various solutions. With the various telephony solutions, it isn’t easy to do an apples-to-apples comparison, but it is possible to know exactly what a company’s investment and costs are with each solution to help make the best decision for how each particular business likes to operate.
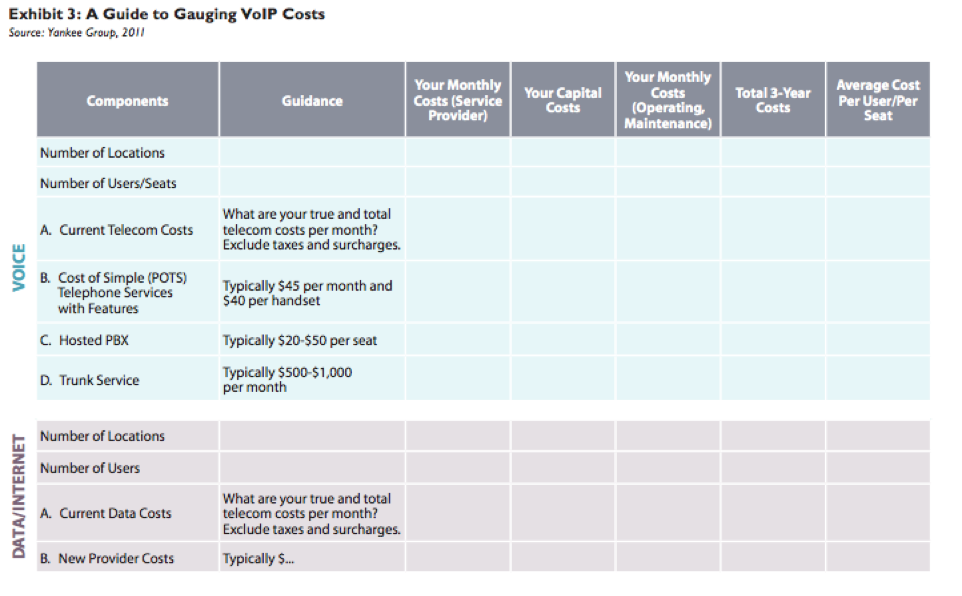
Except in some very specific cases, the cost of a solution is not the sole driving factor, especially when dealing with more complex solutions and services. Once a business has a handle on the costs and infrastructure pieces of the decision as outlined in Exhibit 3, IT decision-makers must consider the qualities of the actual solution provider. Features to consider include:
- The quality and coverage of the trunking service
- The quality and coverage of the underlying network
- Experience in the market and availability of reference accounts
- Interoperability with the major UC vendors
- Deep expertise in trunking solutions and IP communications solutions
- Commercial availability of IP telephony services
- Managed and professional services experience and offerings
VoIP and IP trunking solutions are never going to be one size fits all. Businesses must find the solution that is right for their particular circumstances. Does the business prefer managed/ hosted solutions to premises-based? What are the growth plans? How easy is it to add, remove or change services? What is the state of the current telephony solution? These are just some of the many questions businesses will need to consider, and finding a service provider willing and able to have these discussions and offer business options and flexibility is always a great place to start.
Working with the right service provider partner to deploy a VoIP architecture that leverages IP trunking not only has an impact on costs, but also provides businesses with a road map to other communications and collaboration solutions, such as those found within the UC suite of applications. The right VoIP and UC solution, coupled with the best partner for the business, can lead to a path of change and growth beyond what many traditional communications solutions can enable.
Understanding the Implementation of UC
Communications, collaboration and worker productivity are key components to a business’ competitive advantage. Workers are being challenged to reach more people in shorter periods of time with the right information at hand. To meet these communications demands, many companies are turning to UC, especially as a means to enhance the functionality and use of their IP telephony infrastructure.
UC, in short, brings all a company’s communications and collaborative tools together into one solution. It is the convergence of voice, video, Web and desktop communications built on an IP network and allowing businesses and employees to overcome time, distance and media barriers. UC ultimately enables employees to communicate with each other virtually anywhere, any time and over any device. UC improves the manageability and effectiveness of the ecosystem and makes the enterprise more responsive and agile.
UC consists of the following tools:
- IP telephony/VoIP: VoIP enables companies to use the corporate data network for phone calls rather than having a dedicated network just for telephone service. Historically, VoIP was considered by many organizations as the foundation of UC. However, during the past year, presence and desktop integration have been elevated to being critical to the success of UC.
- Presence: The ability for users to understand one another’s availability and willingness to communicate over a variety of devices is critical in today’s quick-moving business environment. While instant messaging (IM) applications are common today, presence is also being used to understand a user’s status on phones, wireless devices, video conferencing and other collaborative tools. Additionally, presence can be extended to objects such as alarm systems, medical devices and even documents.
- Mobile client: Enterprise mobility is rapidly becoming a key driver for UC. A mobile client mobilizes a UC platform and puts the desktop in the hands of mobile users, which make up 40 percent of the work force. The holy grail of mobility is when a worker can seamlessly access UC applications anytime, on any device.
- Fixed-mobile convergence (FMC): FMC enables a worker to seamlessly move calls between desktop and mobile phones for voice call continuity. As the mobile workforce grows, the ability to provide mobile integration becomes a key decision point for organizations evaluating UC solutions.
- IP network: An IP network is required to deliver information and communications to users. IP is the only protocol that is scalable and simple enough to make the vision of UC a reality; it will be the common network for the deployment of all communications systems. Although IP is a dynamic, scalable technology, it does require ongoing optimization. Management of a network life cycle is critical now as more applications are running on the network.
- Integrated multimedia conferencing: Conferencing applications have existed for a number of years, but only recently have they become integrated into UC. Yankee Group considers the following services multimedia conferencing:
- Video conferencing: Long a nice-to-have, video is now one of the main applications driving UC deployments. Quality and ease of use have improved dramatically, allowing more users to take advantage of video communications.
- Web conferencing: This form of conferencing has become popular within the last five years, due largely in part to ease of use and accessibility. Audio and Web conferencing are now the most widely adopted forms of converged conferencing.
- Audio conferencing: The most mature form of conferencing, audio conferencing through the use of bridge lines is still the most widely adopted form of conferencing. However, as this space evolves, we will see audio become more integrated into other forms of conferencing systems and UC solutions. Yankee Group has seen companies recoup their investment in UC in as little as six months by shedding expensive bridge line services.
Yankee Group believes a strong UC strategy begins with a solid foundation built on a well-planned VoIP environment and leveraging the concept of presence. Exhibit 4 depicts the key components of a full UC and collaboration solution.

UC is valuable on many levels. It is one of the few technologies that can fulfill on the promise of any IT project. Specifically, UC can:
- Lower TCO
- Increase worker productivity
- Create new efficient business processes
- Improve customer satisfaction
Over time, the focus of the value proposition has changed. A few years ago, the primary driver for VoIP and UC revolved around cost savings alone. Though cost savings still remains a key part of the UC decision, especially in tough economic conditions, the real potential is as a foundation for fundamentally changing the business and building long-term competitive advantage. Yankee Group believes we are finally approaching the time when UC solutions will be rapidly adopted by businesses of all sizes as collaboration and communications is poised to take businesses to the next level.
Conclusions and Recommendations
Deploying VoIP and ultimately UC is a key component to transforming into an Anywhere Enterprise®. The business benefits that can be achieved from the flexibility, scalability and functionality of a full IP environment can take business and employee productivity to the next level of success. If deployed strategically, it can also help companies redefine business processes around communications and leapfrog their competition. However, any new technology deployment needs to be a well-planned, strategic initiative with full buy-in at all levels of the organization and the right service provider selection.
Businesses must adopt VoIP and ultimately UC with a view to where their business will be in the future—what technologies and applications are on their road map. Taking into account business expansion, the number of remote and mobile workers, business plans around the customer experience and other possible initiatives all need to be factored into any IP telephony decision. Unlike other technologies, the voice and communications solution chosen by a business today will likely be one that is around for a while. With that in mind, Yankee Group recommends businesses:
- Ensure full support from management executives to run the show. The deployment of VoIP solutions, hosted or on-premises, is not a one-time project. Long-term service commitment and collaboration from the management team is instrumental in achieving a seamless service migration without sacrificing the expected quality of service.
- Choose a solution provider that has a robust IP network as a foundation to the service. For a managed service to provide the necessary levels of reliability and scalability, the data infrastructure needs to be rock solid. An all-IP network will provide high-quality services, newer services faster and a level of reliability that is better than a service built off a hybrid of IP and circuit switching.
- Assess your readiness. UC can be too complex to be deployed across the entire organization in one sweep, especially in larger companies. Find a department or group of workers that would benefit most from UC. A younger group of workers or a highly mobile group is ideal. This will help you establish a strategy for deployment and start a grassroots adoption campaign as UC is slowly rolled out to a wider portion of the company.
- Evaluate service providers on decision criteria that are relevant to this era of communications. Too often, companies make decisions based on vendor incumbency or simply choose the lowest cost provider. UC is ushering in a new era of communications and decision-makers need to evaluate solution providers based on criteria that will enable this transformation. Specifically, organizations should look for the following: Dedicated account managers and project managers to help with the transition, financial stability to ensure investments in UC will continue, full 911 compliance, a one-stop shop for all a company’s communications needs and an aggressive road map of future UC services.
- Do your homework prior to any service-level agreement (SLA)/quality-of-service negotiation. Be ready to compare and analyze SLAs among multiple service providers. Assess your major business-impacting breaches to determine optimal uptime and negotiate business-driven SLAs. Be aware of contract lock-in by setting up baseline service requirements and expectations.
Businesses large and small continue to evolve their communications infrastructure in an attempt to garner the greatest benefits from the latest technologies.
Locked Content
Click on the button below to get access
Unlock NowOr sign in to access all content on Comcast Business Community
Tags
Learn how Comcast Business can help
keep you ready for what's next.










